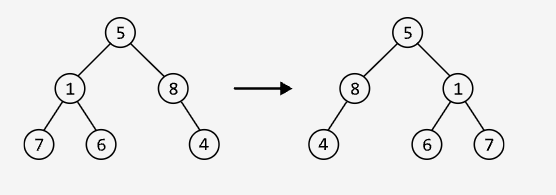
Invert Binary Tree
Easy
Invert a binary tree and return its root. When a binary tree is inverted, it becomes the mirror image of itself.
Example:
Balanced Binary Tree Validation
Easy
Determine if a binary tree is height-balanced, meaning no node’s left subtree and right subtree have a height difference greater than 1.
Example:
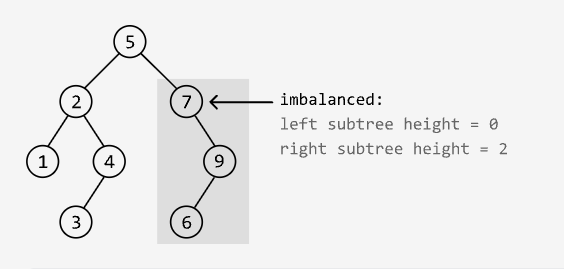
Output: False
Rightmost Nodes of a Binary Tree
Medium
Return an array containing the values of the rightmost nodes at each level of a binary tree.
Example:
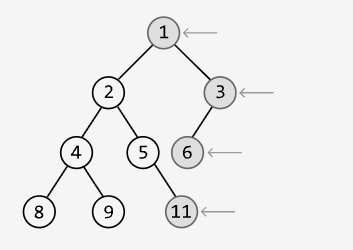
Output: [1, 3, 6, 11]
Widest Binary Tree Level
Medium
Return the width of the widest level in a binary tree, where the width of a level is defined as the distance between its leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes.
Example:
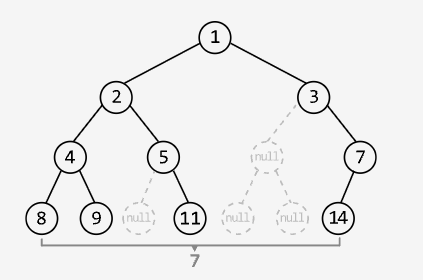
Output: 7
Binary Search Tree Validation
Medium
Verify whether a binary tree is a valid binary search tree (BST). A BST is a binary tree where each node meets the following criteria:
- A node’s left subtree contains only nodes of lower values than the node’s value.
- A node’s right subtree contains only nodes of greater values than the node’s value.
Example:
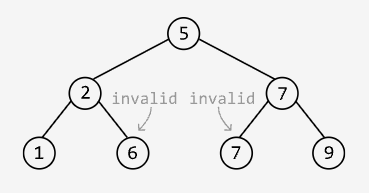
Output: False
Explanation: This tree has two violations of the BST criteria:
- Node 5’s left subtree contains node 6, and node 6’s value is greater than 5.
- Node 7 has a left child with the same value of 7.
Lowest Common Ancestor
Medium
Return the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two nodes, p and q, in a binary tree. The LCA is defined as the lowest node that has both p and q as descendants. A node can be considered an ancestor of itself.
Example:
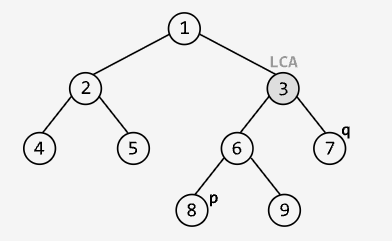
Constraints:
- The tree contains at least two nodes.
- All node values are unique.
pandqrepresent different nodes in the tree.
Build Binary Tree From Preorder and Inorder Traversals
Medium
Construct a binary tree using arrays of values obtained after a preorder traversal and an inorder traversal of the tree.
Example:
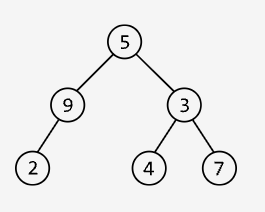
Input: preorder = [5, 9, 2, 3, 4, 7], inorder = [2, 9, 5, 4, 3, 7]
Constraints:
- The tree consists of unique values.
Maximum Sum of a Continuous Path in a Binary Tree
Hard
Return the maximum sum of a continuous path in a binary tree. A path is defined by the following characteristics:
- Consists of a sequence of nodes that can begin and end at any node in the tree
- Each consecutive pair of nodes in the sequence is connected by an edge
- The path must be a single continuous sequence of nodes that doesn’t split into multiple paths
Example:
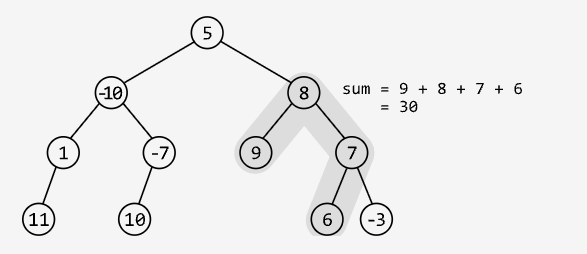
Output: 30
Constraints:
- The tree contains at least one node.
Binary Tree Symmetry
Medium
Determine if a binary tree is vertically symmetric. That is, the left subtree of the root node is a mirror of the right subtree.
Example:
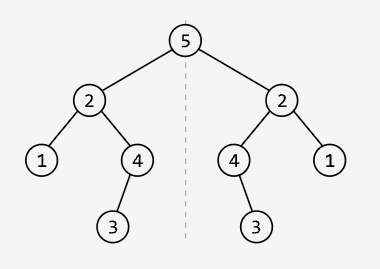
Output: True
Binary Tree Columns
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, return a list of arrays where each array represents a vertical column of the tree. Nodes in the same column should be ordered from top to bottom. Nodes in the same row and column should be ordered from left to right.
Example:
Output: [[2], [9], [5, 1, 4], [3], [7]]
Kth Smallest Number in a Binary Search Tree
Medium
Given the root of a binary search tree (BST) and an integer k, find the kth smallest node value.
Example:
Output: 6
Constraints:
n ≥ 1, wherendenotes the number of nodes in the tree.1 ≤ k ≤ n
Serialize and Deserialize a Binary Tree
Medium
Write a function to serialize a binary tree into a string, and another function to deserialize that string back into the original binary tree structure.
