suma de pares ordenada
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
TestPairSum()
}
func PairSum(data []int, target int) []int {
var result []int
for i, v := range data {
if v >= target {
return []int{}
}
if v+data[i+1] == target {
return []int{i, i + 1}
}
if i+1 == len(data) {
return []int{}
}
}
return result
}
func TestPairSum() {
table := map[uint8]struct {
Input []int
Target int
Want []int
}{
1: {Input: []int{5, -2, 3, 4, 6}, Target: 7, Want: []int{2, 3}},
2: {Input: []int{1, 1, 1}, Target: 2, Want: []int{0, 1}},
3: {Input: []int{2, 7, 11, 15}, Target: 9, Want: []int{0, 1}},
4: {Input: []int{2, 7, 11, 15}, Target: 10, Want: []int{}},
5: {Input: []int{}, Target: 5, Want: []int{}},
6: {Input: []int{5}, Target: 5, Want: []int{}},
7: {Input: []int{5, 5}, Target: 10, Want: []int{0, 1}},
8: {Input: []int{-1, 0, 1, 2, -2}, Target: 0, Want: []int{1, 3}},
9: {Input: []int{-3, 3}, Target: 0, Want: []int{0, 1}},
10: {Input: []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, Target: 9, Want: []int{3, 4}},
11: {Input: []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, Target: 3, Want: []int{0, 1}},
12: {Input: []int{-1, -1, -1, -1, -1}, Target: -2, Want: []int{0, 1}},
}
for k, v := range table {
result := PairSum(v.Input, v.Target)
if v.Want[0] != result[0] && v.Want[1] != result[1] {
fmt.Printf("Error test: %v\n Want:%v Result:%v", k, v.Want, result)
}
fmt.Printf("Test %v:Ok %v \n", k, result)
}
}
sugerencia de gemini
package main
import "fmt"
import "sort"
func PairSum(data []int, target int) []int {
sort.Ints(data) // Aseguramos que el array esté ordenado
left := 0
right := len(data) - 1
for left < right {
sum := data[left] + data[right]
if sum == target {
return []int{left, right}
} else if sum < target {
left++
} else {
right--
}
}
return []int{}
}
type TestCase struct {
Input []int
Target int
Want []int
}
func main() {
testCases := []TestCase{
{Input: []int{-5, -2, 3, 4, 6}, Target: 7, Want: []int{2, 3}},
{Input: []int{1, 1, 1}, Target: 2, Want: []int{0, 1}},
{Input: []int{2, 7, 11, 15}, Target: 9, Want: []int{0, 1}},
{Input: []int{2, 7, 11, 15}, Target: 10, Want: []int{}},
{Input: []int{}, Target: 5, Want: []int{}},
{Input: []int{5}, Target: 5, Want: []int{}},
{Input: []int{5, 5}, Target: 10, Want: []int{0, 1}},
{Input: []int{-1, 0, 1, 2, -2}, Target: 0, Want: []int{1, 3}},
{Input: []int{-3, 3}, Target: 0, Want: []int{0, 1}},
{Input: []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, Target: 9, Want: []int{3, 4}},
{Input: []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, Target: 3, Want: []int{0, 1}},
{Input: []int{-1, -1, -1, -1, -1}, Target: -2, Want: []int{0, 1}},
}
for i, tc := range testCases {
got := PairSum(tc.Input, tc.Target)
sort.Ints(got) // Ordenamos el resultado para comparar correctamente
sort.Ints(tc.Want)
if !equal(got, tc.Want) {
fmt.Printf("Caso %d falló: Input: %v, Target: %d, Got: %v, Want: %v\n", i+1, tc.Input, tc.Target, got, tc.Want)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Caso %d pasó: Input: %v, Target: %d, Got: %v, Want: %v\n", i+1, tc.Input, tc.Target, got, tc.Want)
}
}
}
func equal(a, b []int) bool {
if len(a) != len(b) {
return false
}
for i, v := range a {
if v != b[i] {
return false
}
}
return true
}
Pair Sum – Sorted
Easy
Given an array of integers sorted in ascending order and a target value, return the indexes of any pair of numbers in the array that sum to the target. The order of the indexes in the result doesn’t matter. If no pair is found, return an empty array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-5, -2, 3, 4, 6], target = 7
Output: [2, 3]
Explanation: nums[2] + nums[3] = 3 + 4 = 7
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1, 1, 1], target = 2
Output: [0, 1]
Explanation: other valid outputs could be [1, 0], [0, 2], [2, 0], [1, 2] or [2, 1].
Triplet Sum
Medium
Given an array of integers, return all triplets [a, b, c] such that a + b + c = 0 . The solution must not contain duplicate triplets (e.g., [1, 2, 3] and [2, 3, 1] are considered duplicates). If no such triplets are found, return an empty array.
Each triplet can be arranged in any order, and the output can be returned in any order.
Example:
Input: nums = [0, -1, 2, -3, 1]
Output: [[-3, 1, 2], [-1, 0, 1]]
Is Palindrome Valid
Easy
A palindrome is a sequence of characters that reads the same forward and backward.
Given a string, determine if it’s a palindrome after removing all non-alphanumeric characters. A character is alphanumeric if it’s either a letter or a number.
Example 1:
Input: s = 'a dog! a panic in a pagoda.'
Output: True
Example 2:
Input: s = 'abc123'
Output: False
Constraints:
- The string may include a combination of lowercase English letters, numbers, spaces, and punctuations.
Largest Container
Medium
You are given an array of numbers, each representing the height of a vertical line on a graph. A container can be formed with any pair of these lines, along with the x-axis of the graph. Return the amount of water which the largest container can hold.
Example:
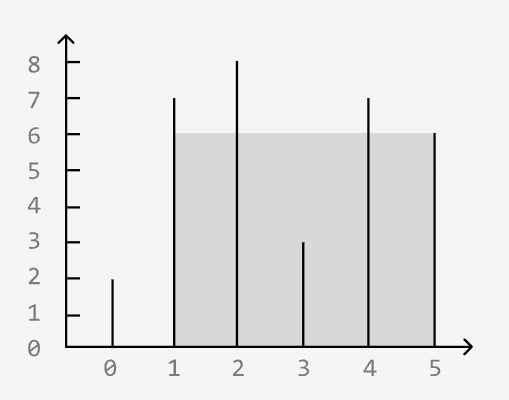
Input: heights = [2, 7, 8, 3, 7, 6]
Output: 24
Shift Zeros to the End
Easy
Given an array of integers, modify the array in place to move all zeros to the end while maintaining the relative order of non-zero elements.
Example:
Input: nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 2]
Output: [1, 3, 2, 0, 0]
Next Lexicographical Sequence
Medium
Given a string of lowercase English letters, rearrange the characters to form a new string representing the next immediate sequence in lexicographical (alphabetical) order. If the given string is already last in lexicographical order among all possible arrangements, return the arrangement that’s first in lexicographical order.
Example 1:
Input: s = 'abcd'
Output: 'abdc'
Explanation: "abdc" is the next sequence in lexicographical order after rearranging "abcd".
Example 2:
Input: s = 'dcba'
Output: 'abcd'
Explanation: Since "dcba" is the last sequence in lexicographical order, we return the first sequence: "abcd".
Constraints:
- The string contains at least one character.