Algoritmos para mejorar tu lógica de programación, el con código en Go
- Amazon Interview | Asteroid Collision | Data Structures & AlgorithmsProblem Statement We are given an array asteroids of integers representing asteroids in a row. The indices of the asteroid in the array represent their relative position in space. For each asteroid, the absolute value represents its size, and the sign represents its direction (positive meaning right, negative meaning left). Each asteroid moves at the… Read more: Amazon Interview | Asteroid Collision | Data Structures & Algorithms
- Cifrado CésarAlgoritmo para el Cifrado Cesar en Go, común cuando inicias en criptografía y fácil de implementar, solo que en momentos de presión puedes llegar a hacer algo complicado cuando en realidad lo puedes resolver con un poco de aritmética (simple).
- Math And GeometrySpiral Traversal Medium Return the elements of a matrix in clockwise spiral order. Example: Reverse 32-Bit Integer Medium Reverse the digits of a signed 32-bit integer. If the reversed integer overflows (i.e., is outside the range [−231−231, 231−1231−1]), return 0. Assume the environment only allows you to store integers within the signed 32-bit integer range. Example 1: Example… Read more: Math And Geometry
- Bit ManipulationHamming Weights of Integers Easy The Hamming weight of a number is the number of set bits (1-bits) in its binary representation. Given a positive integer n, return an array where the ith element is the Hamming weight of integer i for all integers from 0 to n. Example: Explanation: Number Binary representation Number of set bits 0 0 0 1 1 1 2 10 1 3… Read more: Bit Manipulation
- Sort And SearchSort Linked List Medium Given the head of a singly linked list, sort the linked list in ascending order. Example: Sort Array Medium Given an integer array, sort the array in ascending order. Example: Kth Largest Integer Medium Return the kth largest integer in an array. Example: Constraints: Dutch National Flag Medium Given an array of 0s, 1s, and 2s representing red,… Read more: Sort And Search
- GreedyJump to the End Medium You are given an integer array in which you’re originally positioned at index 0. Each number in the array represents the maximum jump distance from the current index. Determine if it’s possible to reach the end of the array. Example 1: Example 2: Constraints: Gas Stations Hard There’s a circular route which… Read more: Greedy
- Dynamic ProgrammingClimbing Stairs Easy Determine the number of distinct ways to climb a staircase of n steps by taking either 1 or 2 steps at a time. Example: Minimum Coin Combination Medium You are given an array of coin values and a target amount of money. Return the minimum number of coins needed to total the target amount. If this isn’t possible,… Read more: Dynamic Programming
- BacktrackingFind All Permutations Medium Return all possible permutations of a given array of unique integers. They can be returned in any order. Example: Find All Subsets Medium Return all possible subsets of a given set of unique integers. Each subset can be ordered in any way, and the subsets can be returned in any order. Example: N Queens Hard… Read more: Backtracking
- GraphsGraph Deep Copy Medium Given a reference to a node within an undirected graph, create a deep copy (clone) of the graph. The copied graph must be completely independent of the original one. This means you need to make new nodes for the copied graph instead of reusing any nodes from the original graph. Example: Constraints: Count… Read more: Graphs
- TriesDesign a Trie Medium Design and implement a trie data structure that supports the following operations: Example: Explanation: Constraints: Insert and Search Words with Wildcards Medium Design and implement a data structure that supports the following operations: Example: Explanation: Constraints: Find All Words on a Board Hard Given a 2D board of characters and an array of… Read more: Tries
- TreesInvert Binary Tree Easy Invert a binary tree and return its root. When a binary tree is inverted, it becomes the mirror image of itself. Example: Balanced Binary Tree Validation Easy Determine if a binary tree is height-balanced, meaning no node’s left subtree and right subtree have a height difference greater than 1. Example: Rightmost Nodes of… Read more: Trees
- Prefix SumsSum Between Range Easy Given an integer array, write a function which returns the sum of values between two indexes. Example: Constraints: K-Sum Subarrays Medium Find the number of subarrays in an integer array that sum to k. Example: Product Array Without Current Element Medium Given an array of integers, return an array res so that res[i] is equal… Read more: Prefix Sums
- IntervalsMerge Overlapping Intervals Medium Merge an array of intervals so there are no overlapping intervals, and return the resultant merged intervals. Example: Constraints: Identify All Interval Overlaps Medium Return an array of all overlaps between two arrays of intervals; intervals1 and intervals2. Each individual interval array is sorted by start value, and contains no overlapping intervals within itself. Example: Constraints: Largest… Read more: Intervals
- HeapsK Most Frequent Strings Medium Find the k most frequently occurring strings in an array, and return them sorted by frequency in descending order. If two strings have the same frequency, sort them in lexicographical order. Example: Explanation: The strings “go” and “byte” appear the most frequently, with frequencies of 3 and 2, respectively. Constraints: Combine Sorted… Read more: Heaps
- StacksValid Parenthesis Expression Easy Given a string representing an expression of parentheses containing the characters ‘(‘, ‘)’, ‘[‘, ‘]’, ‘{‘, or ‘}’, determine if the expression forms a valid sequence of parentheses. A sequence of parentheses is valid if every opening parenthesis has a corresponding closing parenthesis, and no closing parenthesis appears before its matching opening parenthesis. Example 1: Example 2: Explanation:… Read more: Stacks
- Binary SearchFind the Insertion Index Easy You are given a sorted array that contains unique values, along with an integer target. Example 1: Example 2: Explanation: 6 would be inserted at index 4 to be positioned between 5 and 7: [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]. First and Last Occurrences of a Number Medium Given… Read more: Binary Search
- Sliding WindowSubstring Anagrams Medium Given two strings, s and t , both consisting of lowercase English letters, return the number of substrings in s that are anagrams of t. An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of another word or phrase, using all the original letters exactly once. Example: Explanation: There is an anagram of t starting at index 1 (“caabab”)… Read more: Sliding Window
- Fast And Slow PointersLinked List Loop Easy Given a singly linked list, determine if it contains a cycle. A cycle occurs if a node’s next pointer references an earlier node in the linked list, causing a loop. Example: Linked List Midpoint Easy Given a singly linked list, find and return its middle node. If there are two middle nodes, return… Read more: Fast And Slow Pointers
- Linked ListsLinked List Reversal Easy Reverse a singly linked list. Example: Remove the Kth Last Node From a Linked List Medium Return the head of a singly linked list after removing the kth node from the end of it. Example: Constraints: Linked List Intersection Easy Return the node where two singly linked lists intersect. If the linked… Read more: Linked Lists
- Hash Maps And SetsPair Sum – Unsorted Easy Given an array of integers, return the indexes of any two numbers that add up to a target. The order of the indexes in the result doesn’t matter. If no pair is found, return an empty array. Example: Explanation: nums[0] + nums[2] = -1 + 4 = 3 Constraints: Verify Sudoku Board… Read more: Hash Maps And Sets
- Two Pointerssuma de pares ordenada sugerencia de gemini Pair Sum – Sorted Easy Given an array of integers sorted in ascending order and a target value, return the indexes of any pair of numbers in the array that sum to the target. The order of the indexes in the result doesn’t matter. If no pair is found, return an… Read more: Two Pointers
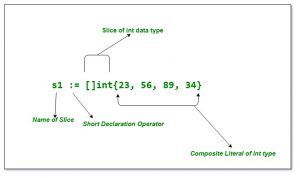
- Operaciones de listas con GoLos arrays y listas son comunes en todos los lenguajes de programación y golang tienes arrays y slices, en cuanto a los Arrays: Tradicionalmente, un array (o arreglo) se refiere a una colección de elementos de tamaño fijo, donde todos los elementos son del mismo tipo Por lo tanto, aunque ambos términos se refieren a… Read more: Operaciones de listas con Go
- Triángulo de pascal en goEn este corto tutorial mostraré como mostrar las primeras N filas del triángulo de pascal. El triángulo de pascal se puede generar de muchas maneras, entre ellas usando el coeficiente binomial El coeficiente binomial que llamaremos nCk(n,k) es una función matemática que retorna entre otros significados: “La cantidad de formas de escoger k elementos de un conujunto de n disponibles. Para imprimir el triángulo de… Read more: Triángulo de pascal en go
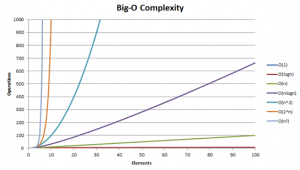
- Notación Bi OLa importancia de saber medir cada algoritmo que implementas O(1) O(long) O(n) O(nlogn) O(n^2) O(2^n) O(n!) Con el pasar del tiempo desarrollamos con más velocidad y vamos conociendo las herramientas en cada uso que les damos, pero no es la primera vez que empiezas a usar herramientas o a implementar código y no sabemos cuanto… Read more: Notación Bi O
- 30 Tipos de algoritmosAlgoritmos de ordenamiento Algoritmos de búsqueda Algoritmos de grafos Algoritmos de árboles Algoritmos de hashing Algoritmos de compresión Algoritmos de encriptación Algoritmos de aprendizaje automático
- Invertir texto con Go en pocas lineasGirar strings o cadenas de texto en Go es algo que nos podemos encontrar en entrevistas o en algún proyecto, aquí tienes 5 ejemplos para que tomes el que más te guste y porsupuesto los tests.
- Algoritmo para sumar todos números de Slice de GoAlgoritmo para sumar todos los números que tiene un Slice de Golang
- Algoritmo para buscar números en un Slice de GoAlgoritmo que busca un número en un Slice de Golang
- Sucesión fibonacci en GoFibonacci secuencia Fibonacci serie Número Fibonacci Ejemplos de la sucesión o serie fibonacci en Golang Primer ejemplo fibonacci Segundo ejemplo fibonacci Este ejemplo muestra la grandeza de Go, para hacer cualquier cosa que tu quieras sin complicaciones y de forma rápida y cómoda para cualquier dev. Tercer ejemplo fibonacci Estructura de directorios Si quieres la… Read more: Sucesión fibonacci en Go
- Arbol
- Slice, Array o Tabla lineal
- Map
- SlicesAnálisis: 1. Primero cree una matriz temporal tempArray más grande que la longitud original de la matriz 2. Desde el principio hasta la posición de inserción Copie cada valor del valor anterior de la matriz a tempArray 3. Desde la posición de inserción hasta cada valor del último elemento Mueva la matriz y moverlo de… Read more: Slices
- Structs