Jump to the End
Medium
You are given an integer array in which you’re originally positioned at index 0. Each number in the array represents the maximum jump distance from the current index. Determine if it’s possible to reach the end of the array.
Example 1:
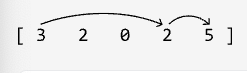
Input: nums = [3, 2, 0, 2, 5]
Output: True
Example 2:
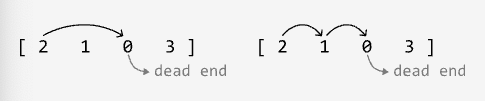
Input: nums = [2, 1, 0, 3]
Output: False
Constraints:
- There is at least one element in
nums. - All integers in
numsare non-negative integers.
Gas Stations
Hard
There’s a circular route which contains gas stations. At each station, you can fill your car with a certain amount of gas, and moving from that station to the next one consumes some fuel.
Find the index of the gas station you would need to start at, in order to complete the circuit without running out of gas. Assume your car starts with an empty tank. If it’s not possible to complete the circuit, return -1. If it’s possible, assume only one solution exists.
Example:
Input: gas = [2, 5, 1, 3], cost = [3, 2, 1, 4]
Output: 1
Explanation:
Start at station 1: gain 5 gas (tank = 5), costs 2 gas to go to station 2 (tank = 3).
At station 2: gain 1 gas (tank = 4), costs 1 gas to go to station 2 (tank = 3).
At station 3: gain 3 gas (tank = 6), costs 4 gas to go to station 3 (tank = 2).
At station 0: gain 2 gas (tank = 4), costs 3 gas to go to station 1 (tank = 1).
We started and finished the circuit at station 1 without running out of gas.
Candies
Medium
You teach a class of children sitting in a row, each of whom has a rating based on their performance. You want to distribute candies to the children while abiding by the following rules:
- Each child must receive at least one candy.
- If two children sit next to each other, the child with the higher rating must receive more candies.
Determine the minimum number of candies you need to distribute to satisfy these conditions.
Example 1:
Input: ratings = [4, 3, 2, 4, 5, 1]
Output: 12
Explanation: You can distribute candies to each child as follows: [3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 1].
Example 2:
Input: ratings = [1, 3, 3]
Output: 4
Explanation: You can distribute candies to each child as follows: [1, 2, 1].