Graph Deep Copy
Medium
Given a reference to a node within an undirected graph, create a deep copy (clone) of the graph. The copied graph must be completely independent of the original one. This means you need to make new nodes for the copied graph instead of reusing any nodes from the original graph.
Example:
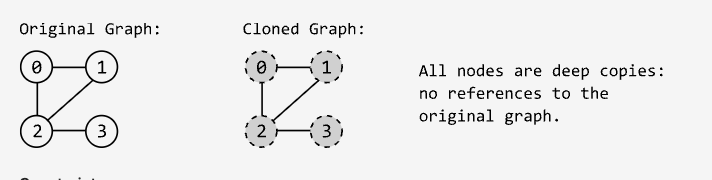
Constraints:
- The value of each node is unique.
- Every node in the graph is reachable from the given node.
Count Islands
Medium
Given a binary matrix representing 1s as land and 0s as water, return the number of islands.
An island is formed by connecting adjacent lands 4-directionally (up, down, left, and right).
Example:
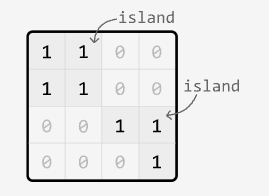
Output: 2
Matrix Infection
Medium
You are given a matrix where each cell is either:
0: Empty1: Uninfected2: Infected
With each passing second, every infected cell (2) infects its uninfected neighboring cells (1) that are 4-directionally adjacent. Determine the number of seconds required for all uninfected cells to become infected. If this is impossible, return ‐1.
Example:
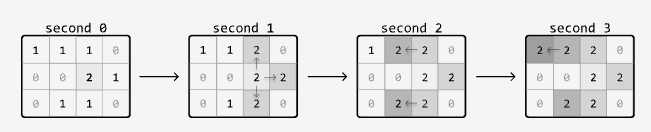
Input: matrix = [[1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 2, 1], [0, 1, 1, 0]]
Output: 3
Bipartite Graph Validation
Medium
Given an undirected graph, determine if it’s bipartite. A graph is bipartite if the nodes can be colored in one of two colors, so that no two adjacent nodes are the same color.
The input is presented as an adjacency list, where graph[i] is a list of all nodes adjacent to node i.
Example:
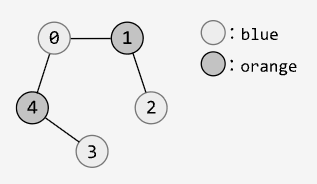
Input: graph = [[1, 4], [0, 2], [1], [4], [0, 3]]
Output: True
Longest Increasing Path
Medium
Find the longest strictly increasing path in a matrix of positive integers. A path is a sequence of cells where each one is 4-directionally adjacent (up, down, left, or right) to the previous one.
Example:
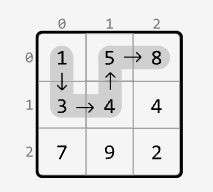
Output: 5
Shortest Transformation Sequence
Hard
Given two words, start and end, and a dictionary containing an array of words, return the length of the shortest transformation sequence to transform start to end. A transformation sequence is a series of words in which:
- Each word differs from the preceding word by exactly one letter.
- Each word in the sequence exists in the dictionary.
If no such transformation sequence exists, return 0.
Example:
Input: start = 'red', end = 'hit',
dictionary = [
'red', 'bed', 'hat', 'rod', 'rad', 'rat', 'hit', 'bad', 'bat'
]
Output: 5
Constraints:
- All words are the same length.
- All words contain only lowercase English letters.
- The dictionary contains no duplicate words.
Merging Communities
Hard
There are n people numbered from 0 to n - 1 , with each person initially belonging to a separate community. When two people from different communities connect, their communities merge into a single community.
Your goal is to write two functions:
connect(x: int, y: int) -> None: Connects personxwith personyand merges their communities.get_community_size(x: int) -> int: Returns the size of the community which personxbelongs to.
Example:
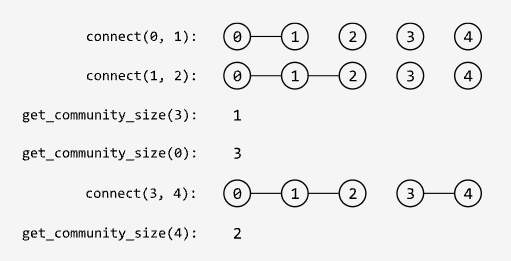
Input: n = 5,
[
connect(0, 1),
connect(1, 2),
get_community_size(3),
get_community_size(0),
connect(3, 4),
get_community_size(4),
]
Output: [1, 3, 2]
Prerequisites
Medium
Given an integer n representing the number of courses labeled from 0 to n - 1, and an array of prerequisite pairs, determine if it’s possible to enroll in all courses.
Each prerequisite is represented as a pair [a, b], indicating that course a must be taken before course b.
Example:
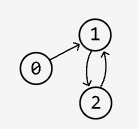
Input: n = 3, prerequisites = [[0, 1], [1, 2], [2, 1]]
Output: False
Explanation: Course 1 cannot be taken without first completing course 2 and, and vice versa.
Constraints:
- For any prerequisite
[a, b],awill not equalb.
Shortest Path
Hard
Given an integer n representing nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 in an undirected graph, and an array of non-negative weighted edges, return an array where each index i contains the shortest path length from a specified start node to node i. If a node is unreachable, set its distance to -1.
Each edge is represented by a triplet of positive integers: the start node, the end node, and the weight of the edge.
Example:
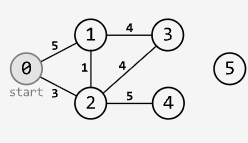
Input: n = 6,
edges = [
[0, 1, 5],
[0, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 1],
[1, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4],
[2, 4, 5],
],
start = 0
Output: [0, 4, 3, 7, 8, -1]
Connect the Dots
Medium
Given a set of points on a plane, determine the minimum cost to connect all these points.
The cost of connecting two points is equal to the Manhattan distance between them, which is calculated as |x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2| for two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
Example:
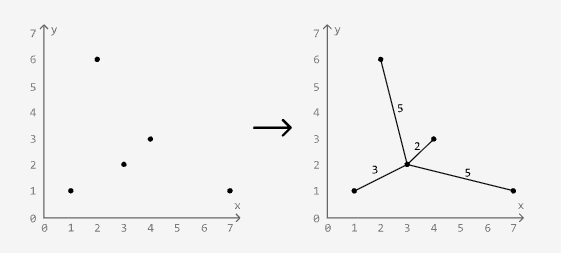
Input: points = [[1, 1], [2, 6], [3, 2], [4, 3], [7, 1]]
Output: 15
Constraints:
- There will be at least 2 points on the plane.