Find the Insertion Index
Easy
You are given a sorted array that contains unique values, along with an integer target.
- If the array contains the target value, return its index.
- Otherwise, return the insertion index. This is the index where the target would be if it were inserted in order, maintaining the sorted sequence of the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9], target = 4
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9], target = 6
Output: 4
Explanation: 6 would be inserted at index 4 to be positioned between 5 and 7: [1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9].
First and Last Occurrences of a Number
Medium
Given an array of integers sorted in non-decreasing order, return the first and last indexes of a target number. If the target is not found, return [-1, -1] .
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11],
target = 4
Output: [3, 5]
Explanation: The first and last occurrences of number 4 are indexes 3 and 5, respectively.
Cutting Wood
Medium
You are given an array representing the heights of trees, and an integer k representing the total length of wood that needs to be cut.
For this task, a woodcutting machine is set to a certain height, H . The machine cuts off the top part of all trees taller than H, while trees shorter than H remain untouched. Determine the highest possible setting of the woodcutter (H) so that it cuts at least k meters of wood.
Assume the woodcutter cannot be set higher than the height of the tallest tree in the array.
Example:
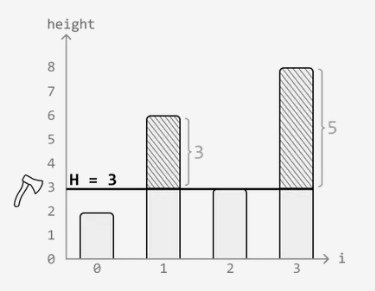
Input: heights = [2, 6, 3, 8], k = 7
Output: 3
Explanation: The highest possible height setting that yields at least k = 7 meters of wood is 3, which yields 8 meters of wood. Any height setting higher than this will yield less than 7 meters of wood.
Constraints:
- It’s always possible to attain at least
kmeters of wood. - There’s at least one tree.
Find the Target in a Rotated Sorted Array
Medium
A rotated sorted array is an array of numbers sorted in ascending order, in which a portion of the array is moved from the beginning to the end. For example, a possible rotation of [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] is [3, 4, 5, 1, 2] , where the first two numbers are moved to the end.
Given a rotated sorted array of unique numbers, return the index of a target value. If the target value is not present, return -1.
Example:
Input: nums = [8, 9, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], target = 1
Output: 2
Find the Median From Two Sorted Arrays
Hard
Given two sorted integer arrays, find their median value as if they were merged into a single sorted sequence.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [0, 2, 5, 6, 8], nums2 = [1, 3, 7]
Output: 4.0
Explanation: Merging both arrays results in [0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8], which has a median of (3 + 5) / 2 = 4.0.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [0, 2, 5, 6, 8], nums2 = [1, 3, 7, 9]
Output: 5.0
Explanation: Merging both arrays results in [0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], which has a median of 5.
Constraints:
- At least one of the input arrays will contain an element.
Matrix Search
Medium
Determine if a target value exists in a matrix. Each row of the matrix is sorted in non-decreasing order, and the first value of each row is greater than or equal to the last value of the previous row.
Example:
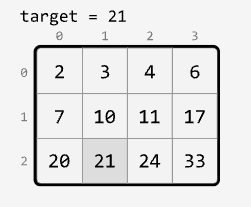
Output: True
Local Maxima in Array
Medium
A local maxima is a value greater than both its immediate neighbors. Return any local maxima in an array. You may assume that an element is always considered to be strictly greater than a neighbor that is outside the array.
Example:
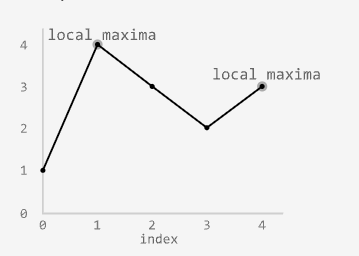
Input: nums = [1, 4, 3, 2, 3]
Output: 1 # index 4 is also acceptable
Constraints:
- No two adjacent elements in the array are equal.
Weighted Random Selection
Medium
Given an array of items, each with a corresponding weight, implement a function that randomly selects an item from the array, where the probability of selecting any item is proportional to its weight.
In other words, the probability of picking the item at index i is:weights[i] / sum(weights).
Return the index of the selected item.
Example:
Input: weights = [3, 1, 2, 4]
Explanation:sum(weights) = 10
3 has a 3/10 probability of being selected.
1 has a 1/10 probability of being selected.
2 has a 2/10 probability of being selected.
4 has a 4/10 probability of being selected.
For example, we expect index 0 to be returned 30% of the time.
Constraints:
- The
weightsarray contains at least one element.